Our Specializations
Testicular

Surgeries
- Radical inguinal orchiectomy
- Orchidectomy
- Testes preserving surgery
- Open/Laparoscopic/ Robotic Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection(RPLND)
Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer is a relatively rare but highly treatable malignancy that affects the testicles. It predominantly strikes young men. Early detection through self-exams and medical screenings is critical for successful outcomes.
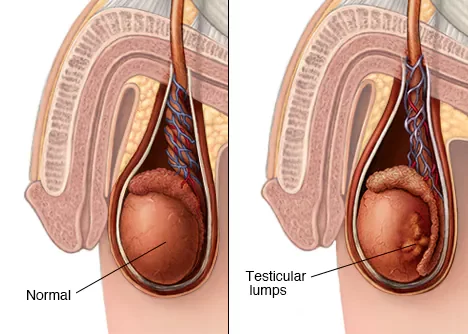
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of testicular cancer include:
- A lump or enlargement in either testicle
- A feeling of heaviness in the scrotum
- A dull ache in the abdomen or groin
- A sudden collection of fluid in the scrotum
- Pain or discomfort in a testicle or the scrotum
- Enlargement or tenderness of the breasts
- Back pain
Causes
It’s not clear what causes testicular cancer in most cases. Doctors know that testicular cancer occurs when healthy cells in a testicle become altered. Healthy cells grow and divide in an orderly way to keep your body functioning normally. But sometimes some cells develop abnormalities, causing this growth to get out of control — these cancer cells continue dividing even when new cells aren’t needed. The accumulating cells form a mass in the testicle.
RIsk Factors
Factors that may increase your risk of testicular cancer include:
An undescended testicle (cryptorchidism)
- Abnormal testicle development
- Family history
- Age
- Race
Prevention
There’s no way to prevent testicular cancer.
Some doctors recommend regular testicle self-examinations to identify testicular cancer at its earliest stage. But not all doctors agree. Discuss testicular self-examination with your doctor if you’re unsure about whether it’s right for you.
Visit Us
Zymus Hospital Address
No.1, K NO. 92, Nanjappa Complex, Kanakapura Rd, Raghuvanahalli, Bangalore City Municipal Corporation Layout, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560062
Menu
Quick Links
Copyright © 2024. Dr Anil Kumar T

