Kidney stones are hard, crystalline deposits that form in the kidneys from minerals and salts in the urine. They can vary in size and may be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball. Passing a kidney stone can be extremely painful, but stones may not cause symptoms until they move into the urinary tract.
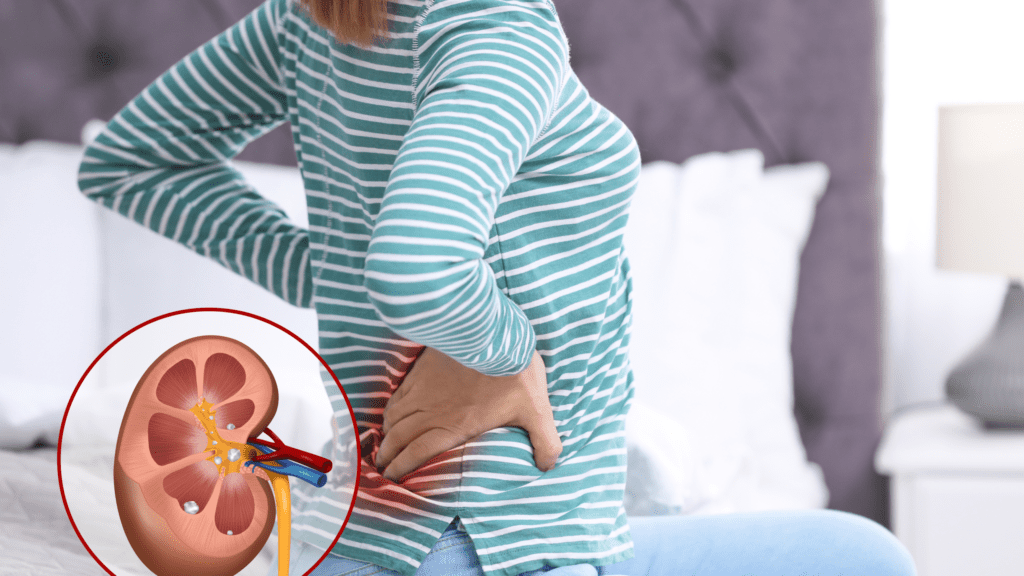
Kidney Stones
Detailed Information
Kidney stones form when the urine becomes too concentrated, allowing minerals to crystallize and stick together. Common causes include:
• Dehydration: Not drinking enough fluids leads to concentrated urine, increasing the likelihood of stone formation.
• Dietary factors: A high intake of salt, sugar, or protein can increase the risk of certain types of kidney stones.
• Medical conditions: Conditions such as obesity, gout, or hyperparathyroidism can increase the risk of kidney stones.
• Genetics: A family history of kidney stones can predispose individuals to develop them.
• Infections: Some types of kidney stones, called struvite stones, can form as a result of urinary tract infections.
• Dehydration: Not drinking enough fluids leads to concentrated urine, increasing the likelihood of stone formation.
• Dietary factors: A high intake of salt, sugar, or protein can increase the risk of certain types of kidney stones.
• Medical conditions: Conditions such as obesity, gout, or hyperparathyroidism can increase the risk of kidney stones.
• Genetics: A family history of kidney stones can predispose individuals to develop them.
• Infections: Some types of kidney stones, called struvite stones, can form as a result of urinary tract infections.
• Severe pain in the back, side, or abdomen (known as renal colic)
• Painful urination.
• Blood in the urine (hematuria).
• Cloudy or foul-smelling urine.
• Nausea and vomiting.
• Frequent urination.
• Fever and chills (if infection is present)
• Painful urination.
• Blood in the urine (hematuria).
• Cloudy or foul-smelling urine.
• Nausea and vomiting.
• Frequent urination.
• Fever and chills (if infection is present)
To prevent kidney stones, consider the following lifestyle changes:
• Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to dilute urine and prevent mineral buildup.
• Dietary adjustments: Reduce salt intake, avoid high-oxalate foods (such as spinach and beets), and limit animal protein if you’re prone to certain types of stones.
• Limit soda and sugary drinks: They can increase the risk of kidney stones, especially those that contain high amounts of sugar and caffeine.
• Citrus fruits: Eating more citrus fruits (such as lemons and oranges) may help prevent stones by increasing the amount of citrate in the urine, which helps prevent stone formation.
• Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to dilute urine and prevent mineral buildup.
• Dietary adjustments: Reduce salt intake, avoid high-oxalate foods (such as spinach and beets), and limit animal protein if you’re prone to certain types of stones.
• Limit soda and sugary drinks: They can increase the risk of kidney stones, especially those that contain high amounts of sugar and caffeine.
• Citrus fruits: Eating more citrus fruits (such as lemons and oranges) may help prevent stones by increasing the amount of citrate in the urine, which helps prevent stone formation.
Treatment for kidney stones depends on their size, type, and location:
• Small stones: Often pass on their own with increased fluid intake and pain relievers.
• Medications: Certain medications, like alpha-blockers, can help relax the muscles in the urinary tract, making it easier to pass the stone.
• Shock wave lithotripsy: A non-invasive procedure that uses sound waves to break up large stones into smaller pieces.
• Ureteroscopy: A thin tube is inserted into the urethra and bladder to remove or break up the stone.
• Percutaneous nephrolithotomy: A surgical procedure used to remove very large stones through a small incision in the back.
• Small stones: Often pass on their own with increased fluid intake and pain relievers.
• Medications: Certain medications, like alpha-blockers, can help relax the muscles in the urinary tract, making it easier to pass the stone.
• Shock wave lithotripsy: A non-invasive procedure that uses sound waves to break up large stones into smaller pieces.
• Ureteroscopy: A thin tube is inserted into the urethra and bladder to remove or break up the stone.
• Percutaneous nephrolithotomy: A surgical procedure used to remove very large stones through a small incision in the back.
Book Your Consultation Now
Schedule an appointment with the leading uro-oncologist in Bangalore, Dr. Anil
Kumar T. Benefit from expert care and advanced treatment options for all your
urological needs, delivered with a patient-centered approach.

Resolve Your Queries
Answers to the most common inquiries about urological conditions, treatments, and patient care. Designed to offer quick guidance and help you better understand, ensuring you feel informed and confident in your healthcare decisions.
Still have queries about Urology & Uro Oncology? Hit the button below.
Accordion Tab Title 2
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Optio, neque qui velit. Magni dolorum quidem ipsam eligendi, totam, facilis laudantium cum accusamus ullam voluptatibus commodi numquam, error, est. Ea, consequatur.
Accordion Tab Title 3
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Optio, neque qui velit. Magni dolorum quidem ipsam eligendi, totam, facilis laudantium cum accusamus ullam voluptatibus commodi numquam, error, est. Ea, consequatur.
Visit Us
Zymus Hospital Address
No.1, K NO. 92, Nanjappa Complex, Kanakapura Rd, Raghuvanahalli, Bangalore City Municipal Corporation Layout, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560062
Menu
Menu
Quick Links
Menu
Copyright © 2024. Dr Anil Kumar T

