Kidney cancer, also known as renal cell carcinoma, is a type of cancer that originates in the kidneys. Here’s some information about the disease, including its causes, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment:
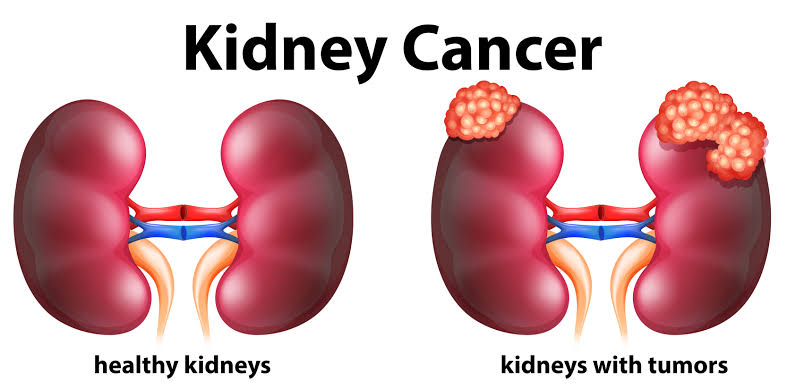
Causes
The exact causes of kidney cancer are not fully understood, but certain risk factors have been identified. These include:
- Age: Kidney cancer is more common in people over the age of 40.
- Gender: Men are more likely to develop kidney cancer than women.
- Smoking: Cigarette smoking is a significant risk factor for kidney cancer.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk.
- High blood pressure: Hypertension is associated with an increased risk of kidney cancer.
- Occupational exposure: Certain occupations, such as those involving exposure to certain chemicals like asbestos or cadmium, may increase the risk.
- Family history: A family history of kidney cancer or certain genetic conditions, such as von Hippel-Lindau disease, increases the risk.
Signs And Symptoms
In the early stages, kidney cancer may not cause any noticeable symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, the following signs and symptoms may occur:
1. Blood in the urine (hematuria)
2. Back or side pain
3. Unintentional weight loss
4. Fatigue
5. Fever
6. Swelling in the legs or ankles
7. Anemia
8. High blood pressure
It’s important to note that these symptoms can be caused by other conditions as well, so it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation.
Diagnosis
To diagnose kidney cancer, a doctor may perform the following:
- Medical history and physical examination: The doctor will ask about symptoms and risk factors and perform a physical examination.
- Imaging tests: Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI can help visualize the kidneys and detect any abnormalities.
- Biopsy: A sample of kidney tissue may be taken for analysis to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
Prevention
While it’s not always possible to prevent kidney cancer, the following measures may help reduce the risk:
1. Quit smoking: If you smoke, quitting can significantly reduce the risk of kidney cancer.
2. Maintain a healthy weight: Adopt a balanced diet and engage in regular physical activity to maintain a healthy weight.
3. Manage blood pressure: Regular check-ups and following your healthcare provider’s recommendations for managing blood pressure can be beneficial.
4. Minimize exposure to harmful chemicals: Take precautions if your occupation involves exposure to substances like asbestos or cadmium.
Treatment
The treatment options for kidney cancer depend on various factors, such as the stage of the cancer, overall health, and individual preferences. Common treatment modalities include:
1. Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor or the entire kidney (nephrectomy) is often the primary treatment for kidney cancer.
2. Targeted therapy: Medications can be used to target specific abnormalities in cancer cells and block their growth.
3. Immunotherapy: These treatments stimulate the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
4. Radiation therapy: High-energy radiation is used to kill cancer cells.
5. Arterial embolization: This procedure blocks the blood supply to the tumor, shrinking it before surgery.
The treatment plan will be determined by a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals based on individual circumstances.It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance regarding kidney cancer, as they can provide the most up-to-date information and recommend appropriate treatments.