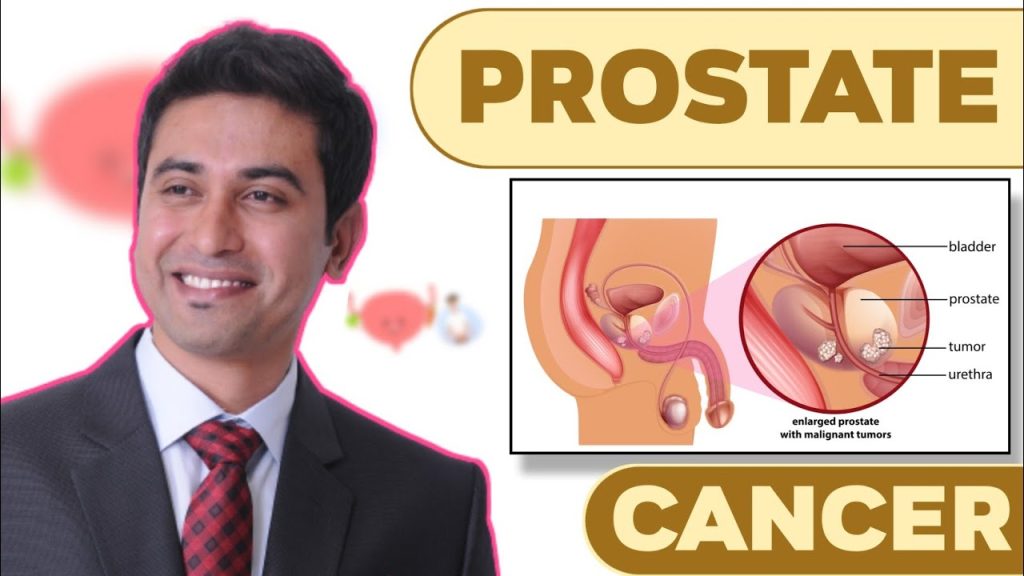
Prostate cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the prostate gland, which is a small walnut-shaped gland located below the bladder in men. The prostate gland produces seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm. Prostate cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the prostate gland start to grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor.
The exact cause of prostate cancer is unknown, but several factors may increase the risk of developing it. These include:
1.Age: The risk of prostate cancer increases with age, particularly after the age of 50.
2. Family history: Having a family history of prostate cancer, especially in a close relative like a father or brother, increases the risk.
3. Genetic factors: Certain inherited gene mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, may contribute to prostate cancer development.
4. Ethnicity: Prostate cancer is more common among African-American men than men of other races.
5. Diet: A diet high in red meat and high-fat dairy products and low in fruits and vegetables may increase the risk

In the early stages, prostate cancer often does not cause any noticeable symptoms. However, as the cancer progresses, the following signs and symptoms may occur
1. Urinary problems: Frequent urination, difficulty starting or stopping urination, weak urine flow, or the need to urinate more often at night.
2. Blood in the urine or semen.
3. Erectile dysfunction or difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection.
4. Pain or discomfort in the pelvic area, lower back, or upper thighs.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by conditions other than prostate cancer. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation.
1. Digital rectal exam (DRE): The doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to feel for any abnormalities in the prostate gland.
2. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test: Elevated levels of PSA in the blood may indicate the presence of prostate cancer, although other factors can also cause PSA levels to rise.
3. Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS): A probe inserted into the rectum emits sound waves to create images of the prostate gland.
4. Prostate biopsy: Small tissue samples are taken from the prostate gland using a needle, and then examined under a microscope to determine if cancer is present.
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent prostate cancer, some lifestyle choices may lower the risk:
1. Healthy diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting the intake of red meat and high-fat dairy products.
2. Exercise regularly: Engage in physical activities like walking, jogging, or cycling for at least 30 minutes a day.
3. Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity has been associated with a higher risk of aggressive prostate cancer.
4. Get regular check-ups: Regular medical check-ups, including prostate cancer screenings, can help detect the disease in its early stages.
The appropriate treatment for prostate cancer depends on various factors, such as the stage of cancer, the aggressiveness of the tumor, and the individual’s overall health. Treatment options may include:
1. Active surveillance: In cases of low-risk prostate cancer, the doctor may monitor the cancer closely without immediate treatment, intervening only if it progresses.
2. Surgery: The surgical removal of the prostate gland, known as a prostatectomy, may be recommended.
3. Radiation therapy: High-energy X-rays or other forms of radiation are used to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors.
4. Hormone therapy: Medications or surgical procedures are used to block