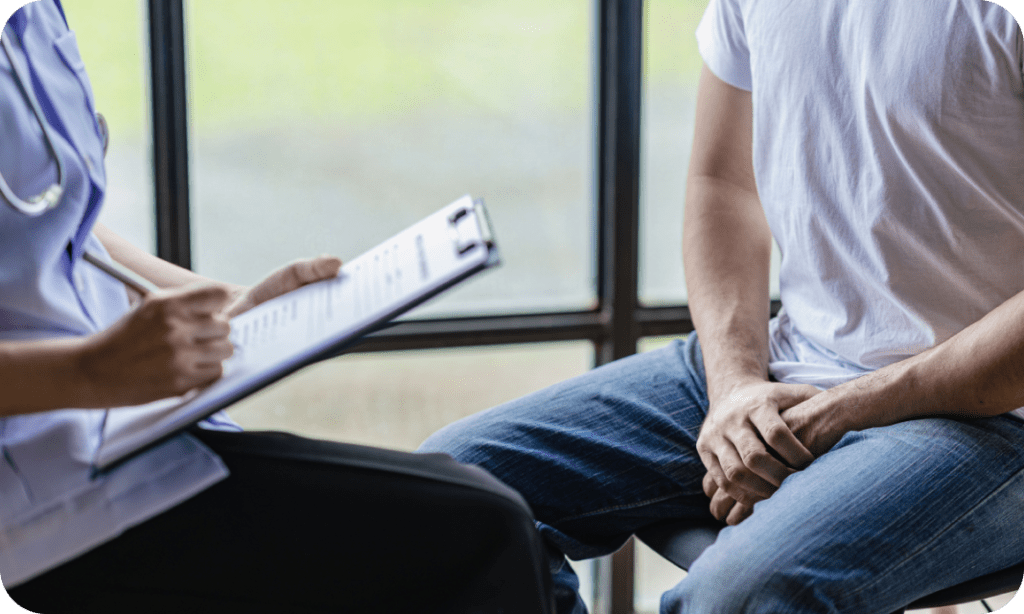
Operating Hours
Monday to Saturday
9:00 AM - 9:00 PM
Contact Us
Call or WhatsApp
Zymus Hospital Address
No.1, K NO. 92, Nanjappa Complex, Kanakapura Rd, Raghuvanahalli, Bangalore City Municipal Corporation Layout, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560062
Menu
Menu
Specialities
Menu
Copyright © 2023. Dr Anil Kumar T