Kidney

Surgeries
- Open/Laparoscopic/ Robotic Simple nephrectomy
- Open/Laparoscopic/ Robotic Partial Nephrectomy
- Open/Laparoscopic/ Robotic Radical Nephroureterectomy and bladder cuff excision
- Open/Laparoscopic/ Robotic ureteric excision
- Laser Excision of ureteral tumour
- Open/Laparoscopic/ Robotic Kidney Cyst surgery
- Open/Laparoscopic/ Robotic pyeloplasty
- Kidney transplantation
Surgeries For Kidney Stone
- Extracorporeal Shockwave Lithotripsy Procedure (ESWL)
- Ureteroscopic Stone Removal
- Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery
- Open Surgery (Pyelolithotomy)
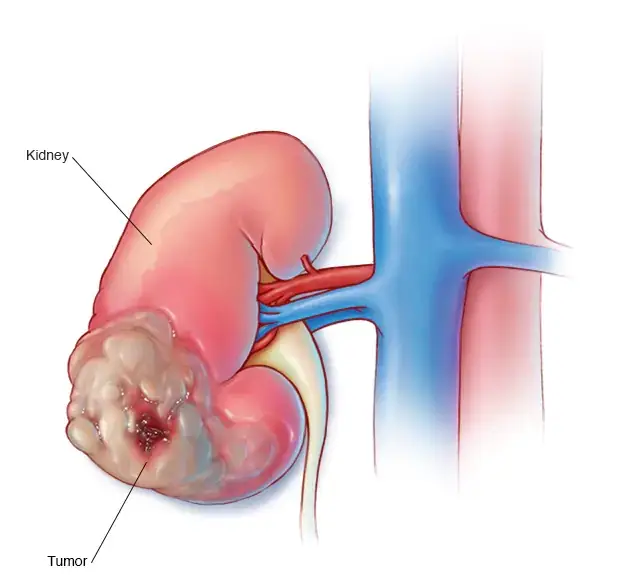
Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cell carcinoma, originates in the kidneys. Risk factors include smoking, obesity, and genetic predisposition. Early detection and advancements in treatment contribute to improved outcomes.
Symptoms
Kidney cancer usually doesn’t have signs or symptoms in its early stages. With time, signs and symptoms may develop, including:
- Blood in your urine, which may appear pink, red or cola colored
- Pain in your back or side that doesn’t go away
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Tiredness
- Fever
Causes
It’s not clear what causes most kidney cancers. Doctors know that kidney cancer begins when some kidney cells develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell’s DNA contains the instructions that tell a cell what to do. The changes tell the cells to grow and divide rapidly. The accumulating abnormal cells form a tumor that can extend beyond the kidney. Some cells can break off and spread (metastasize) to distant parts of the body.
RIsk Factors
Factors that can increase the risk of kidney cancer include:
- Older age
- Smoking
- Obesity
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Treatment for kidney failure
- Certain inherited syndromes
- Family history of kidney cancer
Prevention
Taking steps to improve your health may help reduce your risk of kidney cancer. To reduce your risk, try to:
- Quit smoking
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Control high blood pressure

